A telescopic belt conveyor is a modern material-handling solution designed to improve the efficiency of loading and unloading goods in warehouses, distribution centers, and logistics hubs. Unlike traditional conveyors that remain fixed in one position, this system can extend outward and retract inward to reach different distances. This flexibility allows businesses to move products quickly and safely between storage areas and transportation vehicles such as trucks or shipping containers.
In fast-paced logistics environments, reducing manual handling is essential for maintaining productivity and worker safety. A telescopic belt conveyor uses a sliding mechanical structure that allows multiple conveyor sections to extend smoothly into a vehicle during loading operations. This design helps minimize the need for workers to carry packages over long distances, improving workflow efficiency and reducing fatigue. Many warehouses rely on a telescopic belt conveyor to streamline dock operations and handle large volumes of goods with consistent performance.
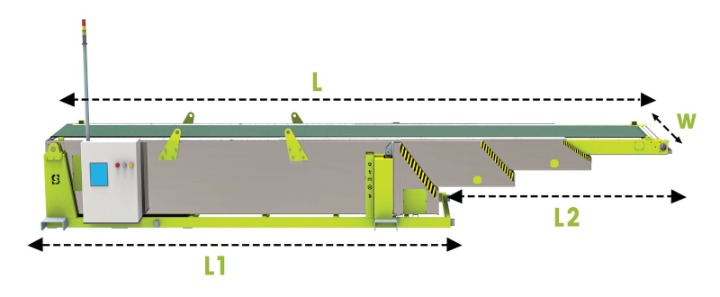
Main Components of a Telescopic Belt Conveyor
Understanding the structure of a telescopic belt conveyor helps explain how it functions in real-world operations. The system is made up of several coordinated components that work together to ensure smooth movement and reliable performance.
The conveyor belt itself is one of the most important parts. Typically made from durable rubber or reinforced PVC material, the belt is designed to carry packages, cartons, and other items safely across the conveyor length. The belt moves continuously during operation, driven by a motorized system.
Another key component is the telescopic frame. This frame consists of multiple nested steel sections that slide within each other. These sections extend forward when needed and retract when the conveyor is not in use. Precision tracks and rollers guide the movement, ensuring stability and alignment during operation.
The drive system powers both the belt movement and the extension mechanism. Electric motors provide controlled motion, while modern systems often include adjustable speed settings to match different loading requirements. Control panels or remote-control units allow operators to manage the extension, retraction, and belt movement easily.
Support structures and adjustable legs are also important. These provide stability and allow the conveyor height to align with loading docks or truck floors, ensuring smooth product transfer.
Working Principle of a Telescopic Belt Conveyor
The operation of a telescopic belt conveyor is designed to be simple yet highly efficient. When a vehicle arrives at a loading dock, the operator activates the extension system. The conveyor gradually slides outward, reaching inside the truck or container. This eliminates the need for workers to move back and forth carrying goods manually.
Once extended, the conveyor belt begins transporting items. During loading, packages are placed on the conveyor at the warehouse end and carried directly into the vehicle. During unloading, workers place items on the extended conveyor inside the truck, and the belt carries them back into the facility.
Sensors and safety controls ensure smooth and secure movement. Limit switches prevent overextension, and emergency stop functions allow operators to halt the system immediately if necessary. After the loading or unloading process is complete, the conveyor retracts into its original compact position.
Benefits of Using a Telescopic Belt Conveyor
One of the most significant advantages of this system is increased operational efficiency. By reducing the distance goods must be carried manually, businesses can load and unload vehicles much faster. This improves turnaround times and supports high-volume shipping operations.
Worker safety is another major benefit. Repetitive lifting and long walking distances can lead to fatigue and injuries. Using a telescopic conveyor reduces physical strain and creates a safer working environment.
Flexibility also makes these conveyors valuable. Since they can extend to different lengths, they can accommodate trucks and containers of various sizes. This adaptability makes them ideal for warehouses handling diverse shipping needs.
Additionally, the consistent movement of the conveyor belt helps reduce product damage. Packages move smoothly along the belt instead of being dropped or mishandled during manual transport.
Common Applications
Telescopic belt conveyors are widely used across multiple industries. Logistics and e-commerce distribution centers depend on them for fast package handling. Courier and postal facilities use them to manage large shipment volumes efficiently.
Manufacturing plants also use telescopic conveyors to move finished goods to shipping areas. Retail distribution centers, airport cargo terminals, and food-processing logistics operations frequently rely on these systems as well.
Maintenance and Safety Considerations
Regular maintenance is essential for reliable performance. Conveyor belts should be inspected for wear, motors should be checked periodically, and moving sections should be properly lubricated. Keeping tracks clean and aligned ensures smooth extension and retraction.
Operator training is equally important. Workers should understand safe loading practices, system controls, and emergency procedures. Preventive maintenance and proper use can significantly extend the equipment’s lifespan.
Conclusion
A telescopic belt conveyor is an efficient and flexible solution for modern material-handling operations. Its extendable design, powered belt system, and user-friendly controls make it ideal for improving loading and unloading processes. By increasing productivity, enhancing safety, and reducing manual labor, telescopic conveyors have become an essential tool in today’s logistics and distribution environments.
George is the voice behind Wisdomised, a news blog dedicated to delivering fresh, engaging stories that keep readers both informed and entertained. With a sharp eye for current events and trending topics, George crafts posts that make complex news accessible and enjoyable. His unique perspective and storytelling skills bring a refreshing twist to every update, inviting readers to explore the world through Wisdomised.